Role of AI in Society, Education, and Health
Research in this axis examines how AI influences information dissemination, social behavior, learning environments, and health outcomes. This includes studying the effects of generative AI on public communication, identifying biases and limitations in real-world AI tools, and developing methods to translate laboratory advances into reliable applications.




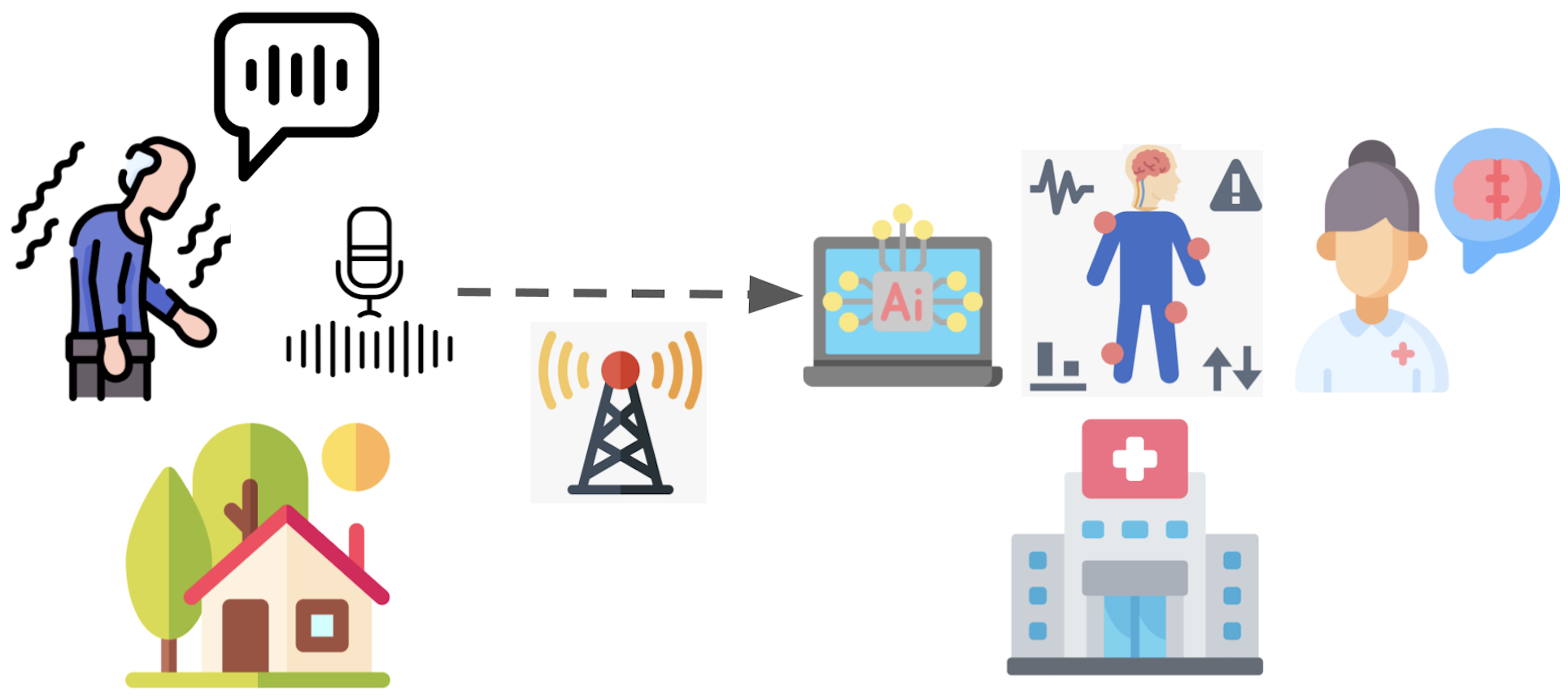 Le suivi de l’évolution de la maladie de Parkinson est complexe car les évaluations actuelles sont souvent coûteuses, longues, et en partie subjectives.
Le suivi de l’évolution de la maladie de Parkinson est complexe car les évaluations actuelles sont souvent coûteuses, longues, et en partie subjectives.